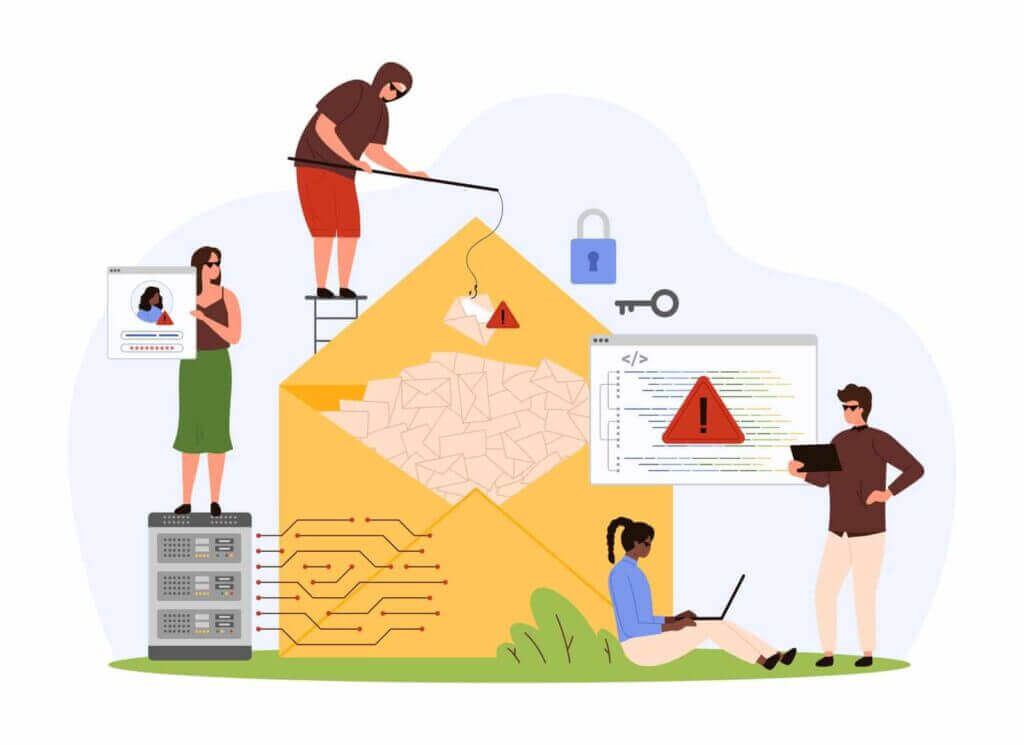
Phishing is an attack executed via email in which cybercriminals use social engineering techniques to trick recipients into divulging sensitive information. A typical phishing email contains a malicious link or attachment that, once clicked, can compromise personal details, such as passwords or social security numbers. These emails are sent out in bulk in phishing campaigns and often masquerade as legitimate communications, employing spoofed sender addresses and logos.
More targeted forms of phishing, such as spear phishing and whaling attacks, focus on individual targets or high-ranking executives within organizations. A Spear phishing attack involves sending a malicious email specifically to an individual or a small group, often based on information gathered through social engineering. A whaling attack targets senior executives and aims for larger monetary gains or sensitive business information.
The key difference between spear phishing and standard phishing lies in the level of personalization;. In contrast, bulk phishing targets large groups with generic messages, and a spear-phishing email is tailored to the victim. Spear phishers use social engineering tactics to make their email message appear more convincing, often mentioning specific details such as the victim’s name or position within a company, which increases the likelihood of a successful breach.
To combat phishing and spear phishing, organizations implement security awareness training programs, conduct phishing simulations, and employ robust security tools. These measures help employees recognize and report suspicious emails, avoiding falling victim to a phishing scam. Email security technologies and vigilant security teams are also crucial in identifying and blocking phishing messages before they reach their intended targets, thus protecting against business email compromise and other malicious activities.
What is Spear Phishing?

Spear phishing is a highly targeted and sophisticated phishing attack in which the attacker sends a spear phishing email to a targeted individual or organization. Unlike regular phishing, which often casts a wide net by sending mass phishing emails, spear phishing targets a specific person or group, making the deception more convincing and harder to detect. These spear phishing emails often appear to come from trusted sources through spoofed email addresses, making them particularly dangerous.
The specificity and targeted nature of spear phishing can significantly increase the success rate compared to regular phishing. This is because spear phishing scams involve intensive research on the target for spear phishing, such as their roles, contacts, and recent activities, allowing the spear phisher to craft a message that appears both genuine and relevant. This targeted approach is why the difference between phishing and spear phishing is crucial for organizations to understand.
Effective spear phishing prevention requires specialized security software and email security tools that can detect and block these targeted threats. Awareness training for employees is also critical, as recognizing spear phishing messages can thwart spear phishing attempts. In the case of spear phishing vs regular phishing, the targeted approach makes spear phishing inherently more challenging to combat, emphasizing the importance of heightened security measures.
The Impact of Spear Phishing on Businesses

The impact of spear phishing on businesses has heightened significantly in recent years. Unlike generic phishing, spear phishing is a targeted attack targeting particular individuals or organizations. These phishing attacks increased in sophistication as attackers performed detailed research on their targets, making their attempts more personalized and harder to detect. This attack often begins with phishing emails that appear trustworthy, manipulating the victim into revealing confidential information.
Spear phishing occurs when an attacker mimics a trusted entity to deceive the victim. The goal of spear phishing is to steal sensitive data or gain access to confidential systems. Spear phishing attacks rely on personal and organizational details, leveraging the collected data to craft more convincing attempts than other spear phishing efforts. Because of the targeted and personalized nature of spear phishing attacks, they are more likely to succeed, causing severe repercussions for businesses.
When successful spear phishing attacks occur, the consequences can be devastating, ranging from financial losses to reputational damage. Such incidents indicate that attackers have done more detailed research than other spear phishing methods, increasing their chances of breaching security defences. As various types of phishing attacks evolve, businesses must stay vigilant and implement robust security measures to mitigate the potential risks of phishing and spear phishing attacks.
Financial Consequences – Direct financial losses

Phishing is a form of cyber attack that can have severe financial consequences. A successful phishing attack can result in direct financial losses, such as stolen funds or unauthorized transactions. Beyond these immediate losses, companies often incur substantial indirect costs, including investigations, legal fees, and security awareness training programs to prevent future phishing attacks. Phishing emails use deceptive tactics to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information, while spear phishing is a type of phishing that specifically targets individuals within an organization.
Spear phishing requires more effort as it involves gathering detailed information about the target to make the attack appear legitimate. Various spear phishing techniques are used, making these attacks highly effective. Responding to a sophisticated spear phishing attack necessitates extensive resources to mitigate damage. Spear phishing takes advantage of personalized approaches, often leading to higher success rates than generic phishing.
Organizations use tools to detect and respond to phishing and spear phishing work attempts. Investing in security measures and protection against phishing is essential. Spear phishing uses targeted communication, making it harder to detect. Therefore, proactive measures, such as security awareness training and phishing simulations, are crucial in preventing attacks.
Data Breaches and Loss of Sensitive Information
Data breaches and the loss of sensitive information present considerable risks, particularly due to the potential for compromised data. One common method that facilitates such breaches involves spear phishing and phishing. While phishing is a broader attack that targets a wide audience with generic bait, spear phishing is more sinister because it targets a specific individual or organization using personalized and convincing spear phishing tactics. Hackers often craft detailed and believable phishing messages that can deceive even the most cautious individuals, leading to unauthorized access and data breaches.
The implications of such breaches can be severe for the affected organization and its customers. When sensitive data is compromised, customer trust and confidentiality are significantly undermined. This can affect the company’s reputation and result in financial loss and legal ramifications. Enterprises are thus investing in advanced security measures that aid in detecting and responding to spear phishing and phishing attacks.
Preventing phishing attacks requires a multifaceted approach, including employee education and deploying robust technological defences. Staff need to be trained to recognize and report suspicious emails and links. Advanced tools are essential for real-time monitoring and alerting on potential threats. Despite these measures, the constant evolution of threat tactics means ongoing vigilance and adaptation are necessary to minimize the risks associated with spear phishing and phishing.
How spear phishing can damage a company’s reputation

Due to its targeted and sophisticated nature, spear phishing can significantly tarnish a company’s reputation. Unlike generic phishing attempts, spear phishing messages may appear to come from trusted sources within the organization, such as colleagues, managers, or partners. When employees inadvertently fall for these deceptive communications, they might reveal sensitive information or download malicious software, leading to data breaches.
Data breach news can spread quickly, eroding customer trust and damaging the company’s public image. Clients and partners may question the firm’s commitment to cybersecurity, doubting its ability to protect confidential information. This can result in a loss of business, as customers may choose to take their patronage elsewhere, fearing for their own data’s safety.
Moreover, internal morale may suffer as employees grapple with the ramifications of the breach, feeling both violated and culpable. This can negatively impact productivity and increase employee turnover rates, further hampering the organization’s stability.
Regulatory bodies may also impose heavy fines and sanctions if the company is found to have inadequate security measures in place. These factors illustrate how spear phishing messages may lead to a cascading series of damages beyond immediate financial losses, inflicting long-term harm to the company’s reputation and operational efficacy.
Common Signs of a Spear Phishing Attack
Spear phishing is a targeted email attack focusing on a specific individual or organization to steal sensitive data, such as login credentials or financial information. Unlike generic phishing attacks broadcast to a wide audience, spear phishing is meticulously crafted to appear legitimate to the targeted recipient. One common sign of a spear phishing attack is highly personalized content, often including the recipient’s name, job title, or specific work-related information. This level of personalization is designed to build trust and make the email seem authentic.
Another red flag is urgent or alarming language that pressures the recipient to take immediate action. For example, the email might claim that there has been suspicious activity on an account and request that the user click a link to verify their information. These links often lead to deceptive websites that capture the victim’s credentials. Additionally, spear phishing emails may include harmless attachments but contain malware to infiltrate the organization’s systems.
Organizations often deploy advanced security measures to combat such attacks, which help detect and analyze suspicious activities and anomalies within the network. This security information and event management tool aggregates and correlates data from various sources to identify threats in real time. Some tools can flag unusual email patterns, such as unexpected communication from external sources or malicious links and attachments.
By remaining vigilant for these common signs and employing robust security tools, organizations can better protect themselves against the sophisticated tactics of spear phishing attacks. Regular employee training and awareness programs also play a vital role in mitigating the risk posed by such targeted threats.
Preventing Spear Phishing Attacks in Your Business
Preventing spear phishing attacks in your business is crucial, as these cyber-attacks specifically target individuals or organizations by pretending to be a trusted source. One effective method in combating this threat is through comprehensive employee training. Educate your staff on recognizing the signs of a spear phishing attack and drill them on the importance of scrutinizing emails, especially those that request sensitive information or immediate actions. Employees should be wary of links or attachments in unsolicited emails, as these could potentially harbour malicious software.
Implementing advanced email security solutions is another key strategy. These solutions use algorithms and artificial intelligence to detect and quarantine suspicious emails. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) can provide an additional layer of security, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access with stolen credentials. Select an email security system that offers real-time threat intelligence, empowering your business to stay ahead of emerging threats.
Regularly updating your software and systems is also essential in preventing spear phishing attacks. Patch management ensures that any vulnerabilities in your software are addressed promptly, reducing the risk of exploitation. Conduct periodic security assessments and simulate phishing attacks to gauge the effectiveness of your current measures. This will help identify any security gaps and improve your defence strategies accordingly.
Finally, cultivating a culture of cybersecurity awareness in your organization can greatly diminish the risks posed by spear phishing attacks. Encourage open communication so that employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious emails or activities. By fostering a vigilant and educated workforce, your business can more effectively counteract the sophisticated tactics employed in spear phishing attacks.




